Why has the cement industry become the main battleground for carbon reduction in China?
The speed of energy consumption reduction is a bit slow, but there are still many ways to reduce carbon and increase efficiency.
In the long run, the cement industry will probably be included in the national carbon trading market.

1 The carbon emission of the industry is only second to that of China and the United States, and clinker production accounts for more than 90% of the total carbon emission of the cement industry mentioned above, covering the whole life cycle of cement.
Therefore, the focus of carbon reduction in the cement industry is also on these two links.
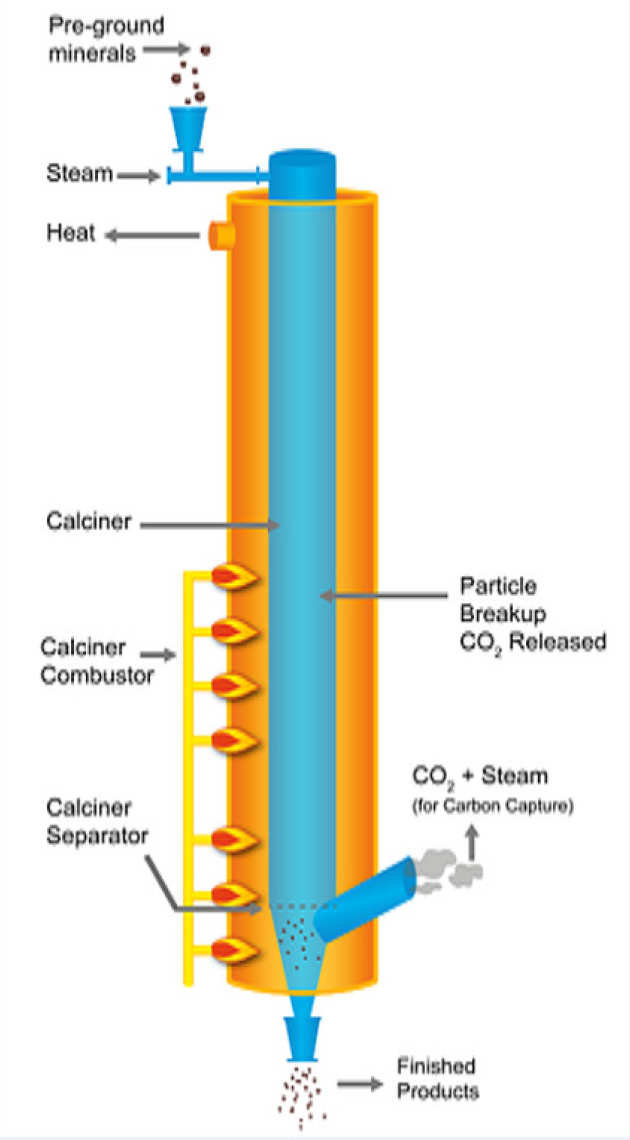
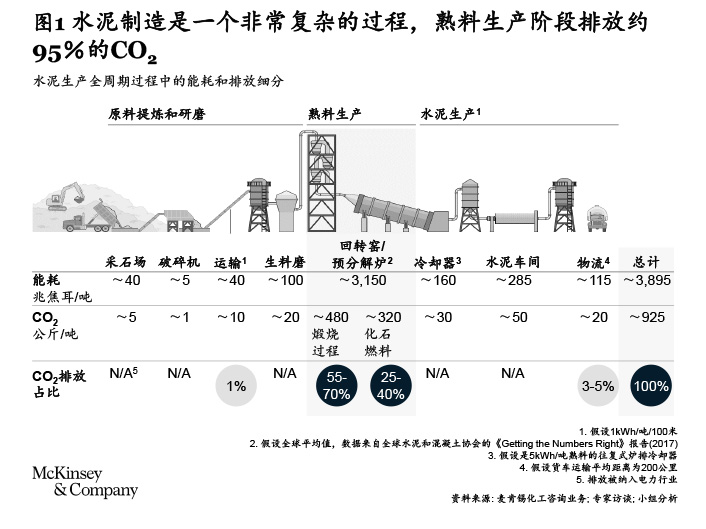
Figure 1 Energy consumption and carbon emissions during the whole cycle of cement production | Figure source [6] 2 Carbon reduction scheme of fuel: from waste heat utilization to green fuel, the utilization efficiency of thermal energy has improved in recent years.
The plan gives three numerical indicators: during the “Fourteenth Five-Year Plan” period, “the comprehensive energy consumption per ton of steel in the steel industry will be reduced by 2%, the energy consumption per unit clinker of cement products will be reduced by 3.7%, and the carbon emission of electrolytic aluminum will be reduced by 5%”.
In 2019, Lafarge announced that half of its rotary kiln fuel in a cement plant in Nigeria was biomass fuel, mainly from agricultural waste, and the company was also trying to dig more fuel from urban solid waste [10].
The plan emphasizes that energy conservation and low carbon action should be fully implemented around carbon peak and carbon neutral target nodes.
One strategy to consider from the source is to reduce the use of fossil fuels or even not use fossil fuels.
Therefore, the country is bound to formulate and issue high standard carbon emission reduction technical requirements for cement production, and the building materials industry should actively respond [1].
The cement industry as a whole contributes about 8% of the global carbon dioxide emissions [4].
This process emits a large amount of carbon dioxide, and the remaining bulk material is mainly composed of calcium silicate, namely clinker.
For carbon reduction, at present, the effect is very limited.
According to the plan, the raw material industry is a typical “high energy consumption, high material consumption and high pollution” industry, and is the key control object of national energy conservation and emission reduction.
This paper discusses some technical solutions being explored by the academia and the industry, or provides possible ideas for the green transformation of the cement industry.
In fact, the practice of adding solid wastes such as tires, organic wastes, sewage sludge and plastics into cement kilns has been around since the 1970s.
.
The clinker is cooled, added with gypsum and auxiliary cementitious materials, and ground into powder, which is cement.
The world produces 3.5 billion tons of ordinary Portland cement every year, and each ton of cement produces 561-622 kg of carbon dioxide.
The carbon emissions of China’s cement industry will account for about 14% of the country’s total carbon emissions [5].
In the whole cement production process, the clinker production stage has the largest carbon dioxide emission, accounting for about 95% of the total production process, more than half of which comes from limestone calcination and less than half from the fuel used in this process [6].
If these waste heat can be recycled and utilized, it can greatly save fuel and reduce carbon emissions.
Both at home and abroad continue to explore fuel substitution and collaborative disposal technologies, expecting to achieve “zero consumption” of fossil energy in clinker production.
How can cement become the main battlefield of carbon reduction alongside steel and electrolytic aluminum? If the cement industry is regarded as a country, it ranks third in the list of carbon emissions, after China and the United States [3].
A case study in India shows that using waste heat for power generation can increase the fuel utilization rate of cement plants by 5% [9].

3.16 The Intellectual cement industry is particularly difficult to transform into a carbon reduction industry | Source: pixabay.com.
Based on this energy consumption, the production of 10 tons of clinker is roughly equivalent to the heat energy consumed by a small apartment in a heating season.
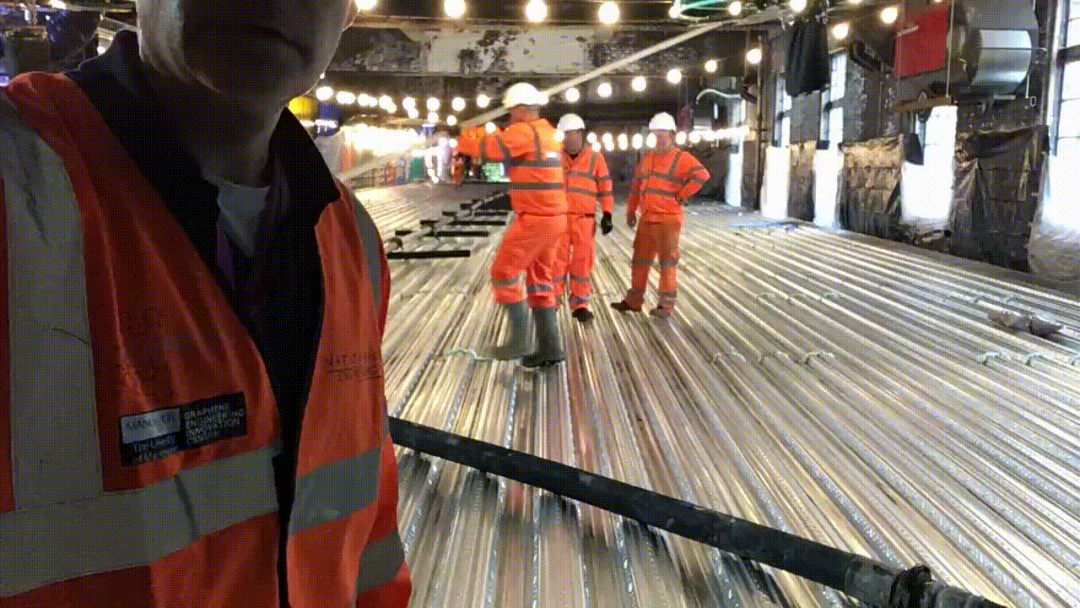
Author | Qu Lijian, Editor-in-chief | Feng Hao ● ● During the two sessions of this year, Hu Shuguang, a member of the National Committee of the Chinese People’s Political Consultative Conference and professor of Wuhan University of Technology, pointed out that the actions and results of carbon emission reduction in the cement industry are directly related to the success or failure of the national “double carbon” strategy.
On December 21, 2021, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, the Ministry of Science and Technology and the Ministry of Natural Resources jointly issued the “Fourteenth Five-Year Plan” for the Development of Raw Materials Industry [2].
One way is to recycle waste heat.
Cement production starts from mining and processing limestone (mainly composed of calcium carbonate), then mixing with clay (mainly composed of silicate), and sending it to 1450 ℃ – 1500 ℃ rotary kiln for calcination.
Therefore, green development of raw material industry is an important part of the plan.

In fact, the policy level has always attached great importance to carbon reduction in the cement industry.
Therefore, the low-carbon transformation of traditional cement industry is of great significance to China and the world.
However, it should also be noted that the current mainstream way of waste heat utilization is power generation.
Since then, according to the data of the International Energy Agency, the energy consumption intensity of clinker production has stagnated at 3.4-3.5 GJ per ton [7].
But now, the mantra of high energy consumption, high material consumption and high pollution industries is getting tighter and tighter.
The world cement looks at China.
To produce 1 ton of clinker, 3.75 GJ will be consumed in 2000 and 3.5 GJ in 2014, with an average annual energy consumption reduction of 0.5% [3].
The high temperature required by the rotary kiln is maintained by the heat generated by fossil fuel combustion, and 44% of this heat will be wasted [8].
In 2020, China’s cement output will be about 2.4 billion tons, accounting for about 60% of the world’s total output.
The carbon-neutral fuel is mainly biomass, because the carbon in biomass will eventually be released, and the carbon in the atmosphere will not be added when used as fuel.
Lafarge, the world cement giant, has been trying to replace fossil fuels with low-carbon and carbon-neutral fuels since 2013.


